-
위상정렬 (Topological Sort)
위상 정렬은 선행 조건들을 가진 일들의 수행 순서를 정한다.
이 순서는 일들의 선행 조건들을 만족시켜야 한다.
예시를 들어보자.
한 학과의 학생들이 수강해야만 하는 7개의 필수 과목들이 있다. (1~7)
어떤순서로 강의를 수강해도 상관이 없지만, 선후수 관계는 만족시켜야한다.
- 2의 선수과목은 1
- 4의 선수과목은 1, 2, 3
- 5의 선수과목은 3
- 6의 선수과목은 2, 4, 5
- 7의 선수과목은 5, 6
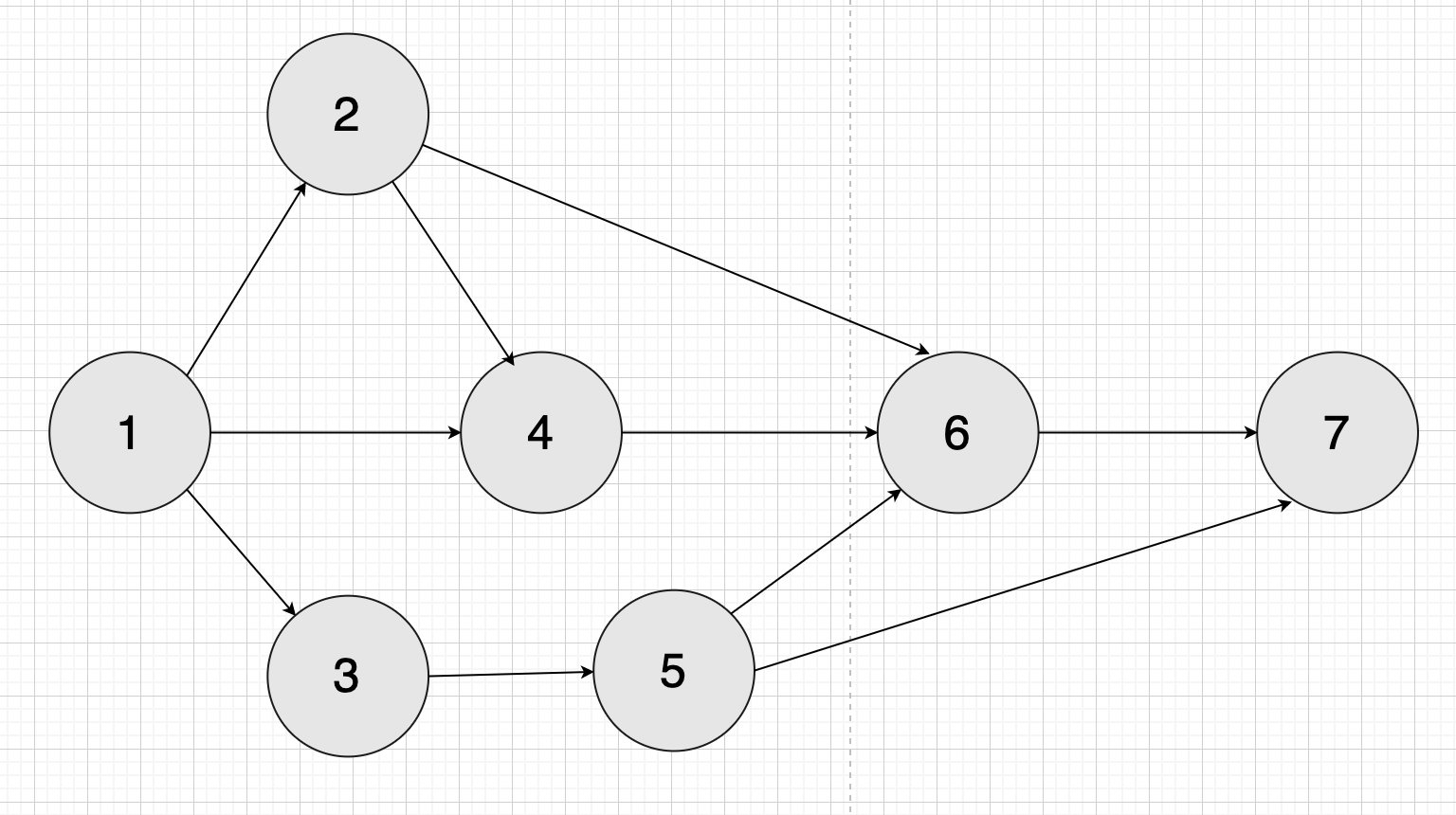
과목들의 선후수 관계도 이 순서에서 그래프의 각 간선 (v, w) 에 대해 v가 w보다 먼저 나와야한다.
이와 같은 순서를 찾는것이
위상정렬이다.조건
- 주어진 방향 그래프에 순환이 없어야 한다. (directed acyclic graph, DAG)
Queue를 이용한 방법
- 진입차수가 0인 정점을 먼저 큐에 넣는다.
- 큐가 빌때까지 반복한다.
- 큐에서 뺀 값 now 를 result 에 추가한다.
- 해당 정점 now 와 연결된 정점들의 진입차수를 1뺀다.
- 새롭게 진입차수가 0이 되는 정점을 큐에 넣는다.
- result 에 들어온 순서대로 출력한다.
위의 그림에 대하여 위상정렬을 해보자.
public class TopologicalSort { static int v = 7; static int[] indegree = new int[v+1]; static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); static void topologicalSort() { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>(); for (int i = 1; i <= v; i++) { if (indegree[i] == 0) { q.offer(i); } } while (!q.isEmpty()) { int now = q.poll(); result.add(now); for (int i = 0; i < graph.get(now).size(); i++) { indegree[graph.get(now).get(i)] -= 1; if (indegree[graph.get(now).get(i)] == 0) { q.offer(graph.get(now).get(i)); } } } System.out.println("위상정렬 순서 출력"); for (Integer integer : result) { System.out.print(integer + " "); } } public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i <= v; i++) { graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>()); } graph.get(1).add(2); indegree[2]++; graph.get(1).add(3); indegree[3]++; graph.get(1).add(4); indegree[4]++; graph.get(2).add(4); indegree[4]++; graph.get(2).add(6); indegree[6]++; graph.get(3).add(5); indegree[5]++; graph.get(4).add(6); indegree[6]++; graph.get(5).add(6); indegree[6]++; graph.get(5).add(7); indegree[7]++; graph.get(6).add(7); indegree[7]++; topologicalSort(); } } // 위상정렬 순서 출력 // 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
※참조
- 자바로 쉽게 배우는 알고리즘
- https://github.com/ndb796/python-for-coding-test
'Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
자료구조 정리 (0) 2021.01.26 비트마스크 (BitMask) (0) 2020.12.09 다이나믹 프로그래밍 정리 (0) 2020.09.09 트리 정리 (0) 2020.09.07 그리디&구현, DFS&BFS (0) 2020.09.01